Getting Started
web-sqlite-js is a friendly, out-of-the-box SQLite database for the web that makes persistent client-side storage simple for every developer.
Designed to be truly effortless, it allows you to get a high-performance relational database running in the browser in seconds. Just install, set your HTTP headers, and start querying—no complex infrastructure required.
Quick start
Before you begin, ensure your environment meets the Browser Compatibility requirements.
Option A: npm / bundler
npm i web-sqlite-jspnpm add web-sqlite-jsyarn add web-sqlite-jsbun add web-sqlite-jsdeno add npm:web-sqlite-jsimport openDB from "web-sqlite-js";
// ...Option B: CDN / script tag (no build step)
For quick demos or plain HTML pages you can load the prebuilt module directly:
<script type="module">
import openDB from "https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/web-sqlite-js@1.0.9/dist/index.js";
// ...
</script>See samples/cdn.html for a copy/paste page you can serve .
Heads up:
SharedArrayBufferrequires COOP/COEP headers; see the section below.
Setup http headers
Pick your stack below to set the headers:
This library depends on SharedArrayBuffer for high performance, which requires your server to send the following HTTP headers:
Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy: same-origin
Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy: require-corpVite
Update your vite.config.ts:
import { defineConfig } from "vite";
export default defineConfig({
server: {
headers: {
"Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy": "same-origin",
"Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy": "require-corp",
},
},
preview: {
headers: {
"Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy": "same-origin",
"Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy": "require-corp",
},
},
});Next.js
Update your next.config.js:
/** @type {import('next').NextConfig} */
const nextConfig = {
async headers() {
return [
{
source: "/(.*)",
headers: [
{
key: "Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy",
value: "same-origin",
},
{
key: "Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy",
value: "require-corp",
},
],
},
];
},
};
module.exports = nextConfig;Webpack (Dev Server)
Update your webpack.config.js:
module.exports = {
// ...
devServer: {
headers: {
"Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy": "same-origin",
"Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy": "require-corp",
},
},
};Nginx
Add the headers to your server block:
server {
# ...
add_header Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy "same-origin";
add_header Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy "require-corp";
# ...
}Express.js
Use a middleware:
const express = require("express");
const app = express();
app.use((req, res, next) => {
res.setHeader("Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy", "same-origin");
res.setHeader("Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy", "require-corp");
next();
});
// ...React / Vue (Create React App / Vue CLI)
Most modern React/Vue setups use Vite. Please refer to the Vite section above.
If you are using an older webpack-based setup (like CRA react-scripts), you technically need to configure the underlying webpack-dev-server, but CRA doesn't expose this easily without ejecting or using tools like craco or react-app-rewired to modify the dev server configuration as shown in the Webpack section.
Usage
Basic Usage
// 1. Open the database (creates 'my-database.sqlite3' in OPFS)
const db = await openDB("local.sqlite3");
// 2. Initialize schema
await db.exec(`
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT,
name TEXT,
email TEXT
);
`);
// 3. Insert data (Parameterized)
await db.exec("INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES (?, ?)", [
"Alice",
"alice@example.com",
]);
await db.exec("INSERT INTO users (name, email) VALUES ($name, $email)", {
$name: "Bob",
$email: "bob@example.com",
});
// 4. Query data
const users = await db.query("SELECT * FROM users");
console.log(users);
// Output: [{ id: 1, name: 'Alice', ... }, { id: 2, name: 'Bob', ... }]
// 5. Close when done
await db.close();Debug mode
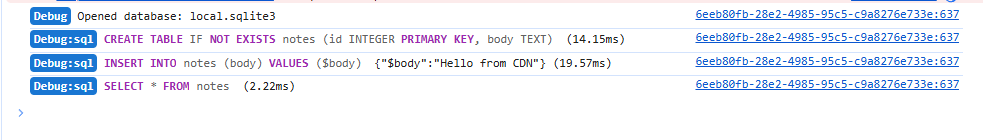
Enable { debug: true } when opening the database to stream worker-side SQL logs (including bind values and timings) to the browser console. It is ideal for profiling and verifying queries during development.
const db = await openDB("local.sqlite3", { debug: true });
await db.exec("CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS notes (body TEXT)");
await db.query("SELECT * FROM notes WHERE id = ?", [1]);The console output highlights SQL keywords and shows the duration of each statement (click to preview):
Transactions
Transactions are atomic. If any command inside the callback fails, the entire transaction is rolled back.
await db.transaction(async (tx) => {
await tx.exec("INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES (?)", ["Charlie"]);
// You can perform multiple operations safely
await tx.exec("INSERT INTO logs (action) VALUES (?)", ["User Created"]);
// If you throw an error here, both INSERTs will be rolled back!
// throw new Error('Something went wrong');
});Logging
For more advanced logging and monitoring, you can subscribe to structured log events from database operations.
Subscribe to Log Events
const unsubscribe = db.onLog((log) => {
console.log(`[${log.level}]`, log.data);
});
// Logs include:
// - SQL execution with timing: {sql: "SELECT * FROM users", duration: 0.28, bind: []}
// - Transaction events: {action: "commit", sql: "COMMIT"}
// - Errors: {error: "SQLITE_CONSTRAINT: UNIQUE constraint failed", sql: "..."}
// - Application events: {action: "open", dbName: "myapp.sqlite3"}
// Later: unsubscribe();Filter by Log Level
db.onLog((log) => {
if (log.level === "error") {
// Send to error tracking service
errorTracker.capture(log.data);
} else if (log.level === "debug") {
// Log SQL execution details
console.log("SQL:", log.data.sql, "Duration:", log.data.duration);
}
});